Structural foaming and structural foam spray are terms used in different contexts, often related to construction, insulation, or manufacturing processes. Here’s an overview of each:

1.Structural Foaming:
2.Construction Context: In construction and civil engineering, structural foaming can refer to the process of injecting foam into cavities or voids within concrete or masonry structures. This foam expands and hardens, providing structural support, improving insulation properties, or reducing weight.
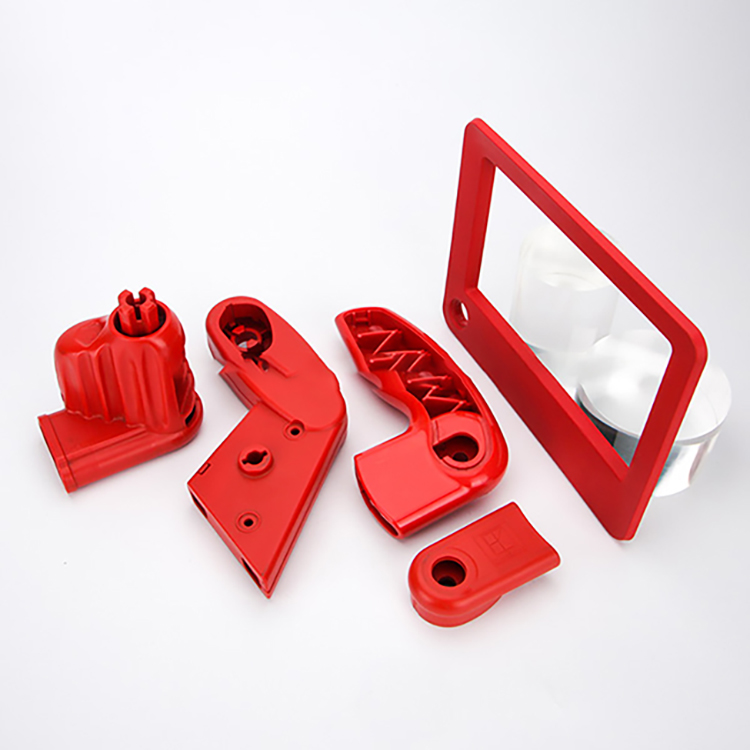
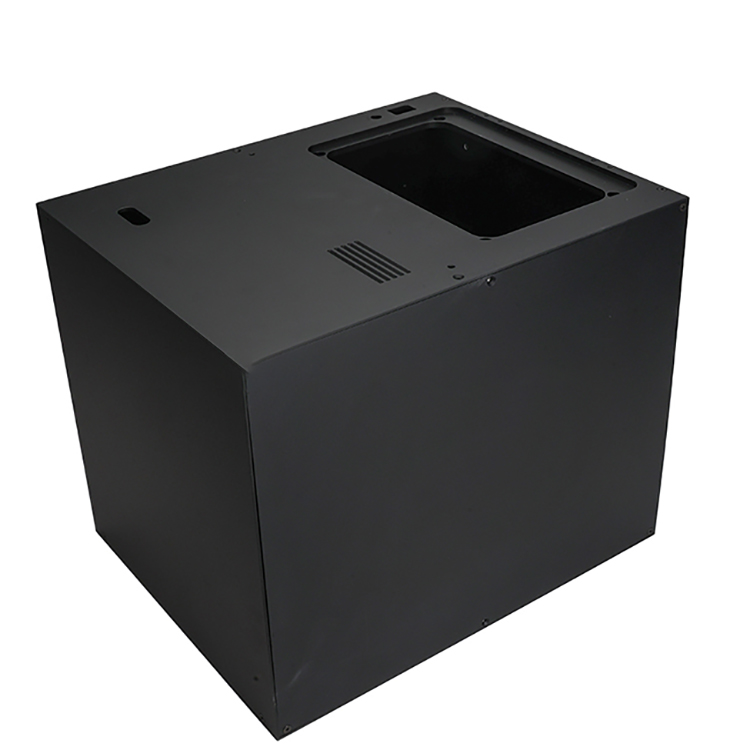
3.Manufacturing Context: In manufacturing, structural foaming may involve injecting a foaming agent into a polymer during molding processes. This creates a cellular structure that enhances strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and insulation properties of the final product.
4.Structural Foam Spray:
5.Insulation: In the building industry, structural foam spray typically refers to spray polyurethane foam (SPF) used for insulation. SPF expands upon application, filling gaps and forming a continuous layer that provides thermal insulation and seals against air infiltration.
6.Manufacturing Applications: Structural foam spray can also be used in manufacturing processes where precise application of foam is needed to create lightweight structures with high strength and durability.
Key Characteristics and Applications:
7.Strength and Lightweight: Structural foam applications generally aim to enhance structural integrity while keeping weight low.
8.Insulation Properties: Foam materials used in these applications often provide thermal and sometimes acoustic insulation benefits.
9.Manufacturing Efficiency: In manufacturing, processes like structural foam injection molding allow for the production of large, lightweight parts with reduced material costs compared to solid parts.
10.Environmental Considerations: The choice of foaming agents and materials used in these processes can affect environmental impact, with increasing emphasis on sustainability and recyclability.
In essence, whether in construction for enhancing structural properties and insulation, or in manufacturing for creating lightweight yet strong components, structural foaming and foam sprays play crucial roles in modern applications where efficiency, performance, and environmental considerations are key factors.